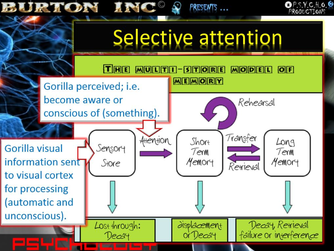
Change blindnessI tried explaining this to my wife yesterday … unfortunately it didn’t get me out of trouble. I dedicate this blog post to her and my IB Psychology student (you know who you are) who asked me if the ‘door experiment’ was a fake. Yesterday I returned home, greeted my wife with a peck on the cheek and began chatting, after a while I realised something was wrong and becoming increasingly more wrong. I’m very perceptive like that. It turns out that she had been out to the hair salon that day and I hadn’t noticed. Perhaps not so perceptive after all. Of course, once she had pointed it out to me, it was immediately obvious. And armed with my Psychology I had an immediate explanation … ‘Gorillas in Our Midst’, a classic experiment by Simons and Chabris (1999). Most people with a passing interest in human behaviour would probably be aware of the experiment. Participants are informed that they will be shown a video of a group of people passing a basketball back and forth between themselves, and that the only thing they are required to do is count the exact number of passes that are made. They are also informed that it wasn’t going to be made easy for them. The individuals in the video would be moving around. There would be two groups passing basketballs, both of them moving around, and participants were to count only the number of passes made by the group wearing white t-shirts. As with much experimentation in Psychology, there was a bit of ‘trickery’ involved. Simons and Chabris weren’t at all interested in the correct number of passes but in whether something that should be blindingly obvious could be made entirely ‘invisible’ with what illusionist term ‘misdirection’. What participants weren’t told was that in the course of the video someone in a gorilla costume would appear, walk between the basketballers, stop, beat its chest and then exit stage left. How many participants would notice the gorilla? Approximately 50 per cent (which is a figure that has been replicated). Half the participants gave the experimenters a completely blank look … “Gorilla? What gorilla?” and many would accuse the experimenters of using two different videos when they were asked to look again. You can’t miss the gorilla when you know the gorilla is going to appear. We have embedded a version of the video shown to participants here. It is well worth showing even if your IB Psychology students are familiar with the study because, not giving too much away, other things are going on which highlight ‘inattentional blindness’. The TED talk by Simons is also very informative. IB Psychology students can relate this experiment to the IB Psychology learning outcome: Evaluate two models or theories of one cognitive process (the cognitive process being memory). One of the more common models to examine is the multistore model of memory (Atkinson & Shiffrin, 1968). As can be seen in the diagram below and according to this model memory consists of the three types of memory stores:
However, as my wife pointed out, this does indeed beg the question, "Why isn't your attention focused on me?" | Inattentional BlindnessShow to your IB Psychology class before you do anything else! Daniel Simon's TED Talkalso called 'change blindness' |
|
Why we can't see what is straight in front of us Insights into an illusionists world, why you didn't notice your wife's new hairstyle and the IB Psychology ERQ - Models of Memory Author: Derek Burton – Passionate about IB Psychology |
IB DipLOMA PsychologY:The IB Psychology Blog. A place to share research and teaching and learning ideas for those studying and teaching Psychology for the IB Diploma Programme. Archives
April 2016
Categories
All
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed